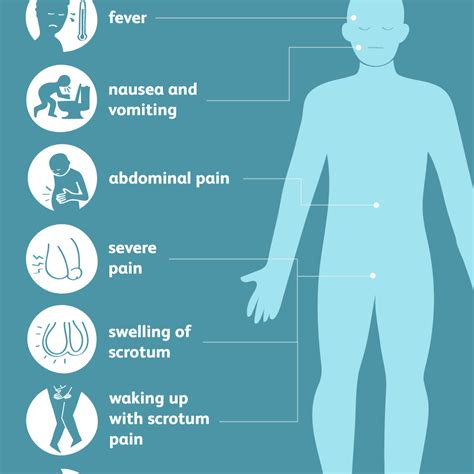
torsion of testes|testicular torsion symptoms in adults : distributor Testicular torsion usually presents with severe testicular pain or pain in the groin and lower abdomen. Pain generally begins suddenly and typically involves only one side. There is often associated nausea and vomiting. The testicle may lie higher in the scrotum due to twisting and subsequent shortening of the spermatic cord or may be positioned in a horizontal orientation. Mild warmth and redness of the overlying area may be present. Elevation of the testicle may worsen . webWhile the rules vary quite a bit across online subcultures, a few have become well established, including a number of holdovers from the original Encyclopedia Dramatica: Rule 1: Do not talk about rules 2-33 Rule 34: There is porn of it. No exceptions. Rule 35: The exception to rule #34 is the citation of rule #34. Rule 36: Anonymous does not .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBExplore Waterford® for exquisite Crystalware, Glasses & Gifts. Experience brilliance and clarity like never before. Shop now!
feuchtigkeitsmessgerät rasen
testicular torsion symptoms in adults
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that occurs when a testicle rotates and cuts off blood flow. Learn about the signs, risk factors, complications and prevention of this condition that affects mostly young boys. See moreTesticular torsion is a serious and painful condition that affects your testicle (s). If you experience testicular torsion, the spermatic cord twists and cuts off blood flow to your testicle. If you don’t .Testicular torsion usually presents with severe testicular pain or pain in the groin and lower abdomen. Pain generally begins suddenly and typically involves only one side. There is often associated nausea and vomiting. The testicle may lie higher in the scrotum due to twisting and subsequent shortening of the spermatic cord or may be positioned in a horizontal orientation. Mild warmth and redness of the overlying area may be present. Elevation of the testicle may worsen .
testicular torsion signs and symptoms
Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that occurs when the spermatic cord twists and cuts off blood flow to the testicle. Learn about the risk factors, diagnosis, and surgical repair of this condition that can cause . Torsion can slow or cut off blood flow to your testicle. A lack of blood makes the affected testicle swell and become painful. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency. You .
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion is caused by the twisting of the blood supply and spermatic cord. The tunica vaginalis is usually solidly adhered to the posterolateral aspect of the testicle, .
The typical symptom of torsion of the testicle (testis) is severe pain that develops quickly - within a few hours, often much more quickly. The pain might be in the lower . Testicular torsion is a urological emergency. A high index of suspicion is important to ensure timely diagnosis and management. Increased public awareness is important in . Testicular torsion is the rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord, which can obstruct its blood supply and lead to necrosis. Most often, testicular torsion affects young adolescents. The most common cause . Testicular torsion is a medical emergency — it occurs when blood flow to the testicle stops, causing sudden and often severe pain and swelling.
Torsion of the appendix testis is a twisting of a vestigial appendage that is located along the testicle. This appendage has no function, yet more than half of all boys are born with one. Although this condition poses no threat to health, it can be painful. Usually no treatment other than to manage pain is needed. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency. Learn what causes your testicle to twist and why you need to treat this condition right away. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency with a 4-6hrs window from the onset of symptoms to salvage the testis before significant ischaemic damage occurs. Any suspected case warrants urgent surgical exploration of the testis to assess the testes and the spermatic cord for evidence of torsion. Torsion of the testicular appendages is considered the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal children and may even be the single most prevalent cause of pediatric orchalgia.[1] Therefore, it should be included in the differential diagnosis for any male presenting with an acute scrotum, particularly in the pediatric age group.[1] Two testicular .
Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, causing . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. .Testicular torsion in a baby happens when the sac around the testicles doesn’t attach to the scrotum. Which children are at risk for testicular torsion? Testicular torsion often occurs in boys ages 10 and older. It can also happen when a baby is growing in the mother's uterus, or shortly after a baby is born. The condition is sometimes seen . Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of .
Testicular torsion is a urological emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischaemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
Testicular torsion is an emergency: When it happens, a guy needs surgery — fast. Saving the testicle becomes more difficult the longer the spermatic cord stays twisted. As a general rule: within about 4–6 hours of the start of the torsion, the testicle can be saved 90% of the time;What is testicular torsion?The testicle has attachments that hold it in place in the scrotum. Occasionally, these attachments do not exist and the testicle can twist. When the testicle twists on itself it causes the blood supply to kink and the testis does not receive the oxygen it needs to live.Who gets testicular torsion?Testicular torsion occurs mainly in two different age
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility.The recommendations on management of testicular torsion are based on the European Association of Urology (EAU) guideline Paediatric urology [Radmayr, 2021], the Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) joint publications Asymptomatic scrotal swelling, commissioning guide [] and Management of paediatric torsion, commissioning guide [], and expert opinion in review . Testicular torsion means that your testicle has rotated in the scrotum. This can wind up the spermatic cord, cutting off blood supply, nerve function, and sperm transport to your scrotum. Torsion of the testes is a surgical emergency, since it causes strangulation of gonadal blood supply with subsequent testicular necrosis and atrophy. Acute scrotal swelling in children indicates torsion of the testes until proven otherwise.
This is called testicular torsion. If testicular torsion occurs, it requires urgent medical attention. What causes testicular torsion and who is at risk? Testicular torsion can happen to boys and men of any age, but most cases occur in .Causes of testicle pain. Sudden, severe testicle pain can be caused by twisting of the testicle (testicular torsion). This is a serious problem that can lead to the loss of the testicle if it's not treated quickly. Less serious causes of testicle pain include: an infection (epididymitis) an injury; an inguinal hernia; a build-up of fluid (cyst)
testicular torsion clinical signs
The appendix testis is a small appendage of normal tissue that is usually located on the upper portion of the testis. The appendix epididymis is a small appendage on the top of the epididymis (a tube-shaped structure connected to the testicle). Torsion of an .
pictures of testicular torsion
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. A thorough history, the presence of a painful and swollen testis and testicular ultrasonography .Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle twists around the cord (the structure extending from the groin to the testes that contains the sperm ducts and blood vessels), like an apple twisting on its stem. When the blood vessels are twisted, they can cut off circulation to the testicle and cause permanent damage, including death of the .Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle twists inside of the scrotum so much that it chokes the blood flow to the testicle. "This leads to sudden, severe pain in the belly and testicle, but guys may try to tough it out or not clearly communicate the symptoms," says Dr. Schlomer.
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours .
feuchtigkeitsmessgerät raumluft test
Intravaginal torsion: hypotheses suggest this occurs because of a congenital abnormality in which the tunica vaginalis attaches to the superior pole of the testis (bell-clapper deformity) → increased mobility of testis within tunica vaginalis, with possible abnormal transverse lie of testis → torsion of the testis (along the spermatic cord) [5] Torsion of the appendix testis (occasionally called torsion of the hydatid of Morgagni) is the most common cause of an acute painful hemiscrotum in a child. The appendix testis is located at the upper pole of the testis (between the .Testicular torsion; Torsion of testis; Clinical Information. An emergency condition caused by the twisting of the spermatic cord which contains the vessels that provide the blood supply to the testis and surrounding structures. It manifests with acute testicular pain. If immediate medical assistance is not provided, it will lead to necrosis and .
feuchtigkeitsmessgerät saturn
Sorteio do "play-off" da UEFA Europa League | UEFA Europa League 2021/22 | UEFA.com. play-off da UEFA Europa League 2023/2024 - calendário do sorteio .
torsion of testes|testicular torsion symptoms in adults